People who first encountered joint diseases often ask: arthritis and arthrosis - what is the difference.These pathologies have similar names and symptoms, so they are often confused.With self -medication, this confusion can cause negative consequences, since what helps with arthrosis with arthritis can harm.
Both of these diseases are serious, lead to disability, so the treatment of joint diseases should be performed by a specialist.
What is the nature of these diseases?
The difference between arthrosis and arthritis is already clear by their names.The suffix “IT” in the name of the disease indicates the inflammatory nature of the disease, and “Oz” - the presence of pathological changes in the tissues.
Accordingly, arthritis is an inflammation of the joint tissue, which can be caused by different causes.And arthrosis is degenerative changes in the joint cartilage, developing after injury or from the action of age -related factors.We will figure out in more detail what arthritis and arthrosis are.
Arthrosis - what is it?
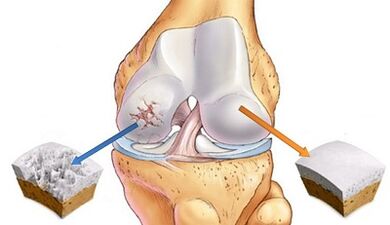
The articulated surfaces of the bones are covered with smooth cartilage tissue and constantly lubricated with synovial fluid for light sliding.Arthrosis is characterized by pathological processes, leading to the fact that the surface of the cartilage loses smoothness, is ulcerated and sophisticated.
Because of this, during the friction of the mating cartilage surfaces, they scratch each other, as a result, degenerative processes are aggravated until the full destruction of the cartilage.Growths appear along the edges of the bone - osteophytes that fetter the mobility of the joint.
With timely detection of arthrosis, the process of destruction of cartilage can be slowed down for decades, using modern methods of treatment and prevention.But, as a rule, in the end, arthrosis leads to the complete destruction of cartilage and immobilization of the affected joint.
The only way to return to it lost functionality is the operation to replace the joint with artificial endoprosthesis.
Arthritis - what is it?
Arthritis is inflammation of the joints.It is known that the inflammatory process is nothing more than the struggle of immune blood cells (leukocytes) with foreign formations in the body.Most often, immune cells are hung up against infection that has fallen.
In the place of this struggle, inflammation occurs, characterized by redness, an increase in local temperature, pain and swelling.Leukocytes who died during the protection of the body are nothing more than pus, often formed in the process of inflammation.
Arthritis can have a different nature.Sometimes it occurs when an infection enters the articular cavity.Such types of arthritis are good to treat antibiotics and often pass without consequences.
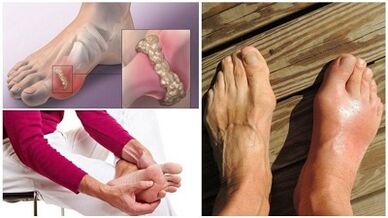
Other types of this disease are worse for treatment and usually lead to disability.In particular, it is rheumatoid arthritis - an autoimmune disease in which immune cells lose their landmarks and begin to fight against tissues of their own body.
Gotric arthritis occurs in the elderly due to a violation of metabolism and deposits in the joints of salts.
Psoriatic arthritis, which is found in approximately 10% of patients with psoriasis, as well as many other types of this dangerous disease.
Is there a relationship between these diseases?
Disassembleing how arthrosis differs from arthrosis, one cannot but mention that these diseases often accompany each other.So, for example, with rheumatoid arthritis, articular tissues are subjected to degenerative changes characteristic of arthrosis.Over time, the joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis are deformed and lose their functions, as with arthrosis.
Similar can be said about gouty arthritis.Sharp crystals of salts, which were deposited in articular cartilage, on the one hand, cause their inflammation, and on the other, they scratch the surfaces of the cartilage, which causes its abrasion and gradual degeneration characteristic of arthrosis.
As you can see, the chronic forms of arthritis negatively affect the condition of the joint cartilage and over time lead to the progression of processes characteristic of arthrosis - deformation and the loss of joint functions.
This rule works the other way.The course of arthrosis is rarely complete without concomitant arthritis.When the surfaces of the articular cartilage, destroying due to degenerative processes, rub against each other, microtraumas appear on them, pieces of cartilage can be abandoned.This provokes inflammatory processes, and we already know that inflammation in the joints is arthritis.
Thus, arthrosis occurs with periodic exacerbations, which are often accompanied by joined arthritis.
Due to the fact that these two diseases are so interconnected, it is sometimes difficult to understand: arthritis and arthrosis-what is the difference.To decide, you need to look at the root cause of the disease, at what the pathological process is launched.If the impetus of the disease has become degenerative changes in the cartilage, then this is arthrosis, and if the cause in inflammations caused by infections, problems with hormonal background, immunity or metabolism, then this is arthritis.
What are the causes of these pathologies?
Arthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic change in cartilage that develop for reasons:
- Insufficient tissue nutrition;
- Traumatic nature.
The lack of nutrition occurs, as a rule, due to age -related changes in the body.Therefore, arthrosis often appears in people over 50-60 years old.At this age, tissue regeneration slows down, violations in metabolic processes appear, which in many leads to problems with the joints.
A traumatic arthrosis can develop at a younger age.Its cause is congenital as well as acquired defects on joint cartilage, which injure the surface of the mating cartilage, which provokes their further destruction.
The primordials of traumatic arthrosis can become:
- Congenital defects of the articular cartilage;
- Injuries received;
- Surgical operations on the joints;
- A large excess of body weight.
Arthritis, unlike arthrosis, with the exception of gouty, is more often found in young people.Its reasons are:
- Genetic predisposition to autoimmune and systemic diseases;
- Infections;
- Hormonal disorders.
What is the similarity and difference in symptoms?
Arthrosis is characterized by a gradual, slow increase in symptoms.The initial stage of the disease can last years, without showing itself.A crunch in the joints may be felt, periodically occurring pain at a load above the usual one.
Most often, the doctor is addressed when the disease has already reached the II stage.Characteristic symptoms of arthrosis:
- Joint pain under load, subsides at rest;
- Clicks when moving the problem joint;
- Morning stiffness, when, after waking up for the normal operation of the joint, it is necessary to “develop” it;
- Most often, the joints of the brushes, stop, spine, knee and hip are susceptible to arthrosis;less often - shoulder and ankle;
- The appearance of pain in rest, night pain indicates an attached arthritis-inflammation due to constant microtrauma of the cartilage;
- In the later stages, a progressive decrease in the amplitude of movements joins, up to the complete immobilization of the joint, or, conversely, the appearance of "decaying", unnatural mobility.

Not an example of arthrosis, arthritis begins with pronounced symptoms characteristic of inflammation processes:
- Severe pain in the joint, not even subsided at rest, feel pulsation, twitching;
- Night pains that do not allow to fall asleep;
- Redness, swelling in the defeat zone;
- High temperature at the site of inflammation, often an increase in temperature of the whole body;
- Small joints are more susceptible to arthritis - wrists, fingers, sometimes ankle, knees;
- Several joints (polyarthritis) are often affected simultaneously;
- Often arthritis becomes a complication of diseases caused by bacterial and viral infections.
The rest of the symptoms of arthritis varies depending on its species, of which there are many.Many types of arthritis are serious diseases that affect other body systems in addition to joints.
Diagnostics
For the doctor, the difference between arthritis and arthrosis is obvious by the clinical picture.Often, in order to diagnose arthrosis and establish its stage, it is enough to make an X -ray of the problematic joint in two projections.The picture will show the value of the articular gap, the presence or absence of bone growths - osteophytes, the degree of bone deformation.
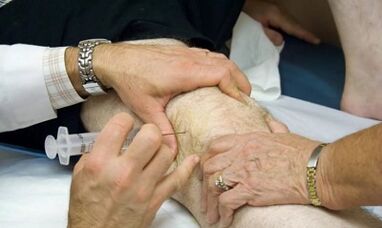
Diagnosis of arthritis requires more studies, because for successful treatment it is necessary to establish a type of pathology - whether a systemic disease is a system, whether inflammation is caused by infection or exacerbation of arthrosis.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, such modern diagnostic methods as ultrasound, CT, MRI, arthroscopy, joint puncture for the study of synovial fluid can be used.Of great importance in the diagnosis of arthritis is a blood test for rheumen.
Similarity and difference in therapy
Treatment of arthritis and arthrosis has more differences than similarities.Almost, the only thing that unites them is the use of non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to eliminate pain and inflammation.Depending on the diagnosis and condition of the patient, these drugs can be used for local application, orally, or in the form of injections, including the articular cavity.
With the ineffectiveness of the treatment of NSAIDs, hormonal drugs are used - corticosteroids that have strong side effects, so they are prescribed only in extreme cases.
Otherwise, therapy of arthritis and arthrosis varies.Each type of arthritis has its own treatment regimen that takes into account the nature of the disease.In therapy of each type, in addition to NSAIDs, antibiotics, hormonal, immunobiological drugs and many other specific drugs, including physiotherapeutic ones, can be used.
The main goal of the treatment of arthritis is to relieve inflammation, therapy of concomitant diseases and ensure a long period of remission.In cases of severe damage to the joints, surgical operations are indicated.
In the treatment of arthrosis, the main task is to slow down the pathological processes of destruction of the joint cartilage.For this, chondroprotectors are actively used - drugs that contribute to the regeneration of joint cartilage, as well as vitamins and minerals.In the remission stage, patients are shown physiotherapeutic procedures, physiotherapy exercises.

Of great importance is attached to prevention measures:
- Normalization of weight;
- Proper full nutrition;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Refusal to overload sore joints;
- Feasible motor activity.
Upon reaching severe stages of arthrosis due to the immobility of the joint or vice versa-unnatural mobility can be lost to the functionality of the limb.In such cases, the patient will help to return to a full -fledged life operation to replace the damaged joint with an endoprosthesis.
Unfortunately, there are no therapeutic agents that can restore the joints destroyed by arthrosis and arthritis.It is only possible to stretch this pathological process as much as possible in time, and after the failure of the joint, resort to surgical intervention.Therefore, it is very important not to delay the visit to the doctor, noting the first signs of these diseases.
As you can see, the difference between arthritis and arthrosis determines the differences in their treatment.Arthritis therapy is focused on eliminating the inflammatory process and the treatment of concomitant diseases, and in the treatment of arthrosis, the relief of pain and the prevention of further destruction of the joints come first in the treatment of arthrosis.
In this context, it becomes clear how to relate to warming the joints in these diseases.Heating of the problem area helps to activate blood circulation in nearby tissues.
With degenerative-dystrophic processes in cartilage tissue, the blood flow improves the joint of oxygen and nutrients, accelerates metabolic processes.This helps to improve joint tissue regeneration.So, with arthrosis, warming of the joints is useful.
Heating pads and warming compresses for arthritis have a completely different effect.In the zone of the inflammatory process, the temperature is already increased.Heating only exacerbates the inflammatory process and promotes the spread of infection outside the joint.Therefore, with arthritis, heating of sore joints with heating pads, compresses and baths is strictly prohibited.
Conclusion
Many people are interested in: what is worse than arthritis or arthrosis.This question may seem strange, because it is impossible to choose an easier disease.Both the disease are associated with severe pain, restrictions on motor activity.Arthrosis and many types of arthritis lead to disability.
But if only joints are affected with arthrosis, then, for example, with rheumatoid arthritis, not only joints suffer, but, practically, all systems of the body-cardiovascular, nervous, respiratory, kidneys, leather, hematopoiesis, organs of vision.
With any of these diseases, it is important to recognize them in the initial stages and start treatment as soon as possible in order to slow down the progression of these pathologies, while the damage caused by the joints is not too large.



































